Let’s cut to the chase: If you’re reading this, it means you’re concerned about diabetes. Maybe you know someone with diabetes, or maybe you have it yourself. Maybe you just want to learn more about the disease and how to prevent or manage it. If your blood sugar is too high, you have type 2 diabetes; if your blood sugar is too low and you need insulin shots, that would be type 1 diabetes. In both cases — and any combination of them — being informed will help. Even if you don’t know exactly what type of diabetes you have right now, let us help put you on the path to a healthier life.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic (lifelong) condition in which your blood sugar, or blood glucose levels are too high. Blood glucose comes from the foods we eat and provides energy for the cells in our bodies. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, which often occurs during childhood, and type 2 diabetes, which accounts for about 90 percent of all diabetes cases. Scientists don’t know what causes type 1 diabetes, but they think type 2 diabetes is linked to being overweight and having a poor diet. Most people can control diabetes with diet and exercise, along with medications and insulin injections in some cases. Knowing your risk for diabetes and what to do about it is key to keeping your blood sugar in a healthy range, preventing, or reversing the damage diabetes can cause to your body, and living a long and healthy life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
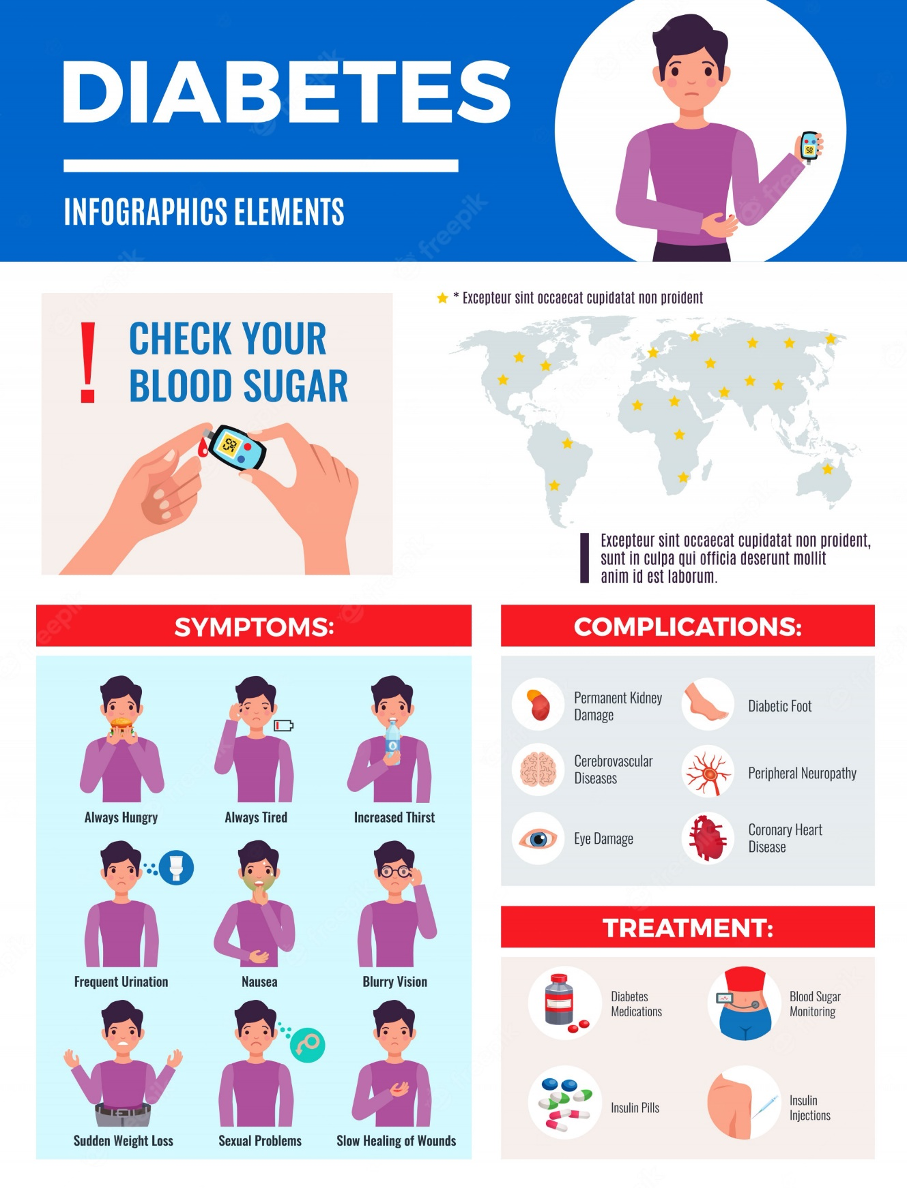
If you have diabetes, it’s important to know what the symptoms are and what to do about them. People with diabetes might not notice symptoms right away because they affect their bodies over time. If you’re not monitoring your blood sugar and you’re not being treated, these can turn into serious health problems.
Type 2 diabetes: Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can include:
- Increased hunger
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Blurry vision
- Tiredness
- Sores that are slow to heal
It may also cause recurring infections. This is because elevated glucose levels make it harder for the body to heal.
How to control Diabetes
There is no cure for diabetes, but you can control it by keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary. The key to controlling your diabetes is to keep your blood sugar in a healthy range. This will help prevent complications from diabetes, like heart disease, blindness, kidney disease, and amputations. You’ll also be better able to manage your weight, which is important for people with diabetes and for people trying to prevent diabetes.
Healthy eating is a central part of managing diabetes. In some cases, changing your diet may be enough to control the disease.
Type 2 diabetes: Eating the right types of foods can both control your blood sugar and help you lose any excess weight. Carb counting is an important part of eating for type 2 diabetes. A dietitian can help you figure out how many grams of carbohydrates to eat at each meal.
Managing your weight and diet as a diabetic

There’s no one diet that’s recommended for everyone with diabetes. You should work with your doctor to create a diet and exercise plan that’s right for you. The American Diabetes Association suggests following a diet that is high in fiber, low in saturated fats, and low in sugar, salt, and processed foods. You should also get regular physical activity. You may need to adjust your diet to keep your blood sugar in a healthy range. In order to keep your blood sugar levels steady, try to eat small meals throughout the day. Emphasize healthy foods such as:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean protein such as poultry and fish
- Healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts

11 Best Low-Sugar Fruits
- Lemons (and limes)
- Raspberries
- Strawberries
- Blackberries:
- Kiwis
- Grapefruit
- Avocado
- Watermelon
- Cantaloupe
- Oranges
- Peaches
The Most Nutrient-Dense Vegetables
- Spinach
- Carrots
- Broccoli
- Garlic
- Brussels sprouts
- Kale
- Green peas
- Beets
- Asparagus
- Red cabbage
- Sweet potatoes
- Collard greens
- Cauliflower
Health Benefits of Eating Whole Grains
Common varieties of whole grains include:
- Oatmeal
- Popcorn
- Millet
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Whole rye
- Wild rice
- Wheat berry
- Bulgur
- Buckwheat
- Freekeh
- Barley
- Sorghum
Products made from these foods are considered whole grains. These include certain types of bread, pasta, and breakfast cereals. When you purchase processed whole-grain products, read the ingredient list to make sure they’re made entirely from whole grains, not a mixture of whole and refined grains.
Also, keep an eye on the sugar content, especially in the case of breakfast cereals, which are often loaded with added sugar. Seeing “whole grain” on the packaging does not automatically mean that the product is healthy.
12 Best Types of Fish to Eat
- Alaskan salmon
- Cod
- Herring
- Mahi-mahi
- Mackerel
- Perch
- Rainbow trout
- Sardines
- Striped bass
- Tuna
- Alaskan pollock
- Char
Exercise for people with Diabetes
Exercising is crucial for anyone, and doubly so for those with blood sugar issues — or at risk of diabetes. You can improve your overall health and help prevent diabetes-related complications. Studies show that people who are physically active have a lower risk of developing diabetes than those who are not physically active. Exercise can also help control your blood sugar levels and help you lose weight if you’re overweight. You can exercise at any time and any place, indoors or out, thanks to health apps, on-demand fitness classes, and social media fitness challenges. You can also hire a personal trainer to work with you in person or remotely to design a safe and effective exercise program. Exercise can lower your blood sugar in two ways: by making your body more sensitive to insulin so your cells will take in more glucose in the blood, and by helping you lose weight since being overweight can increase your risk for type 2 diabetes.

Our last word: you should make eating healthier and getting regular physical activity a priority in your life. If you need help making these changes, talk to your doctor about how to do it healthfully and in the long term. Make sure you’re staying hydrated, which is key when it comes to keeping your blood sugar levels stable. A healthy diet and exercise program will help you lower your blood sugar level and manage diabetes.